Product Name: Five copper silicide (Cu5Si)
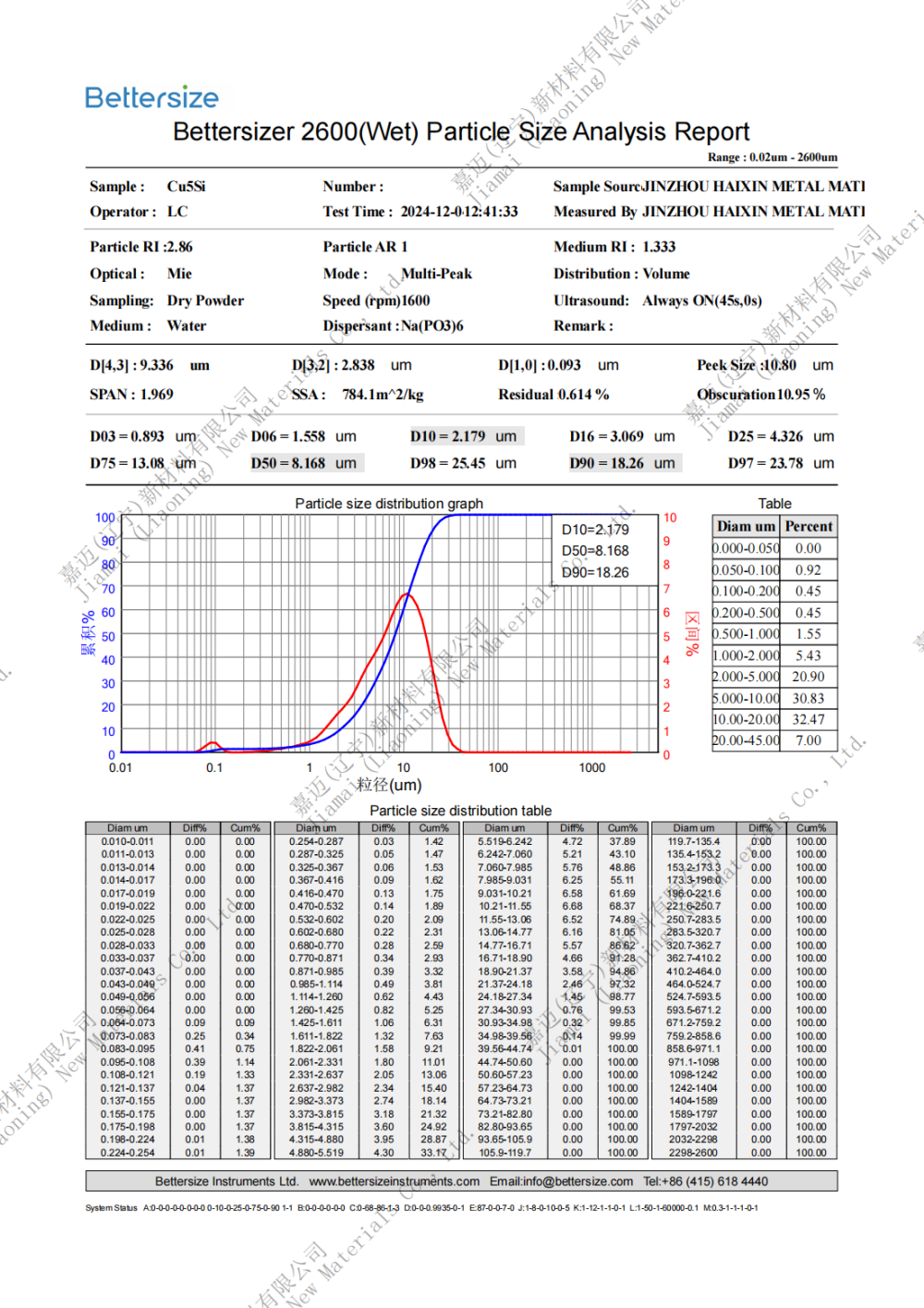
Specification: 0.8-10um (D50)
Appearance: Irregular
Color: Black Grey
Features: high hardness, high density, excellent conductivity, thermal conductivity, ductility, corrosion resistance, wear resistance
Application: Electronic components, optoelectronic devices, aerospace, materials science, thermal management and other fields




Copper silicide
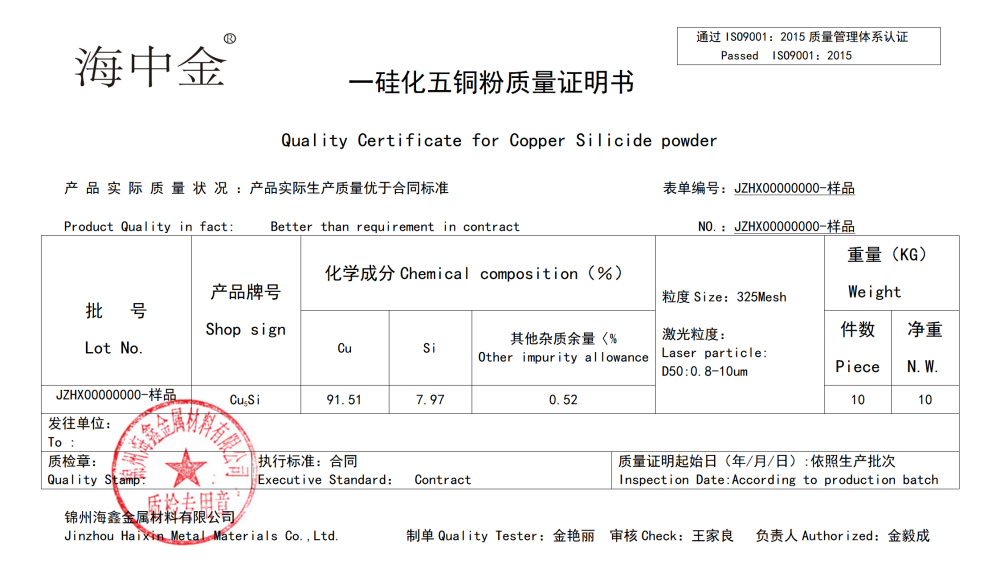
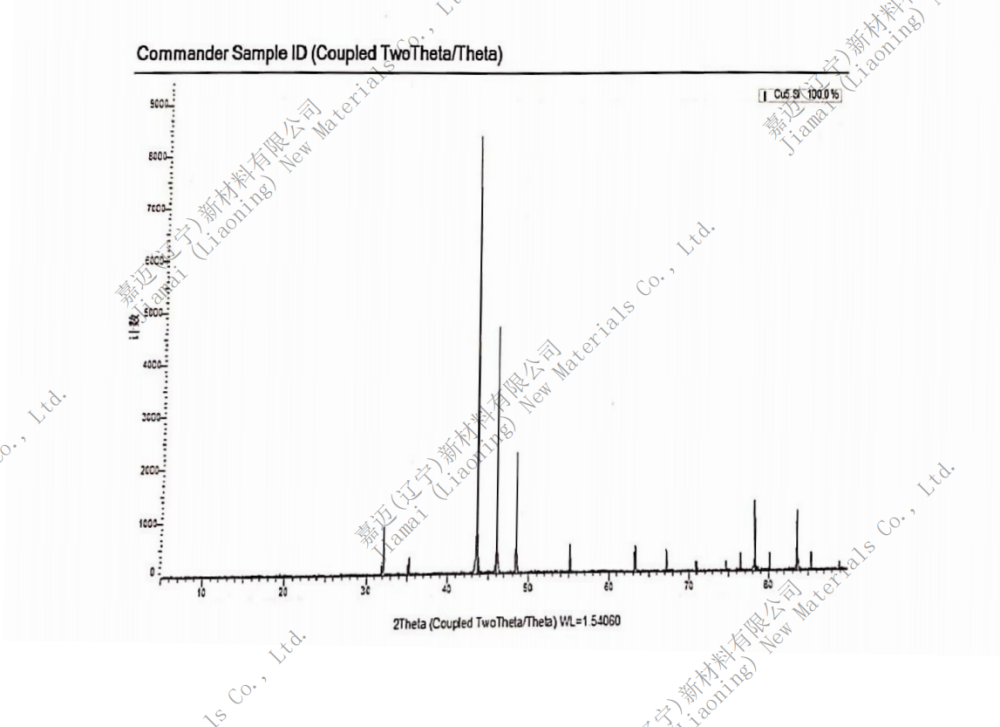
Molecular formula: Cu5Si
CAS Number: 12159-07-8
EINECS Number: 235-286-8
Color/Appearance: Grey Powder
Molecular weight: 345.81
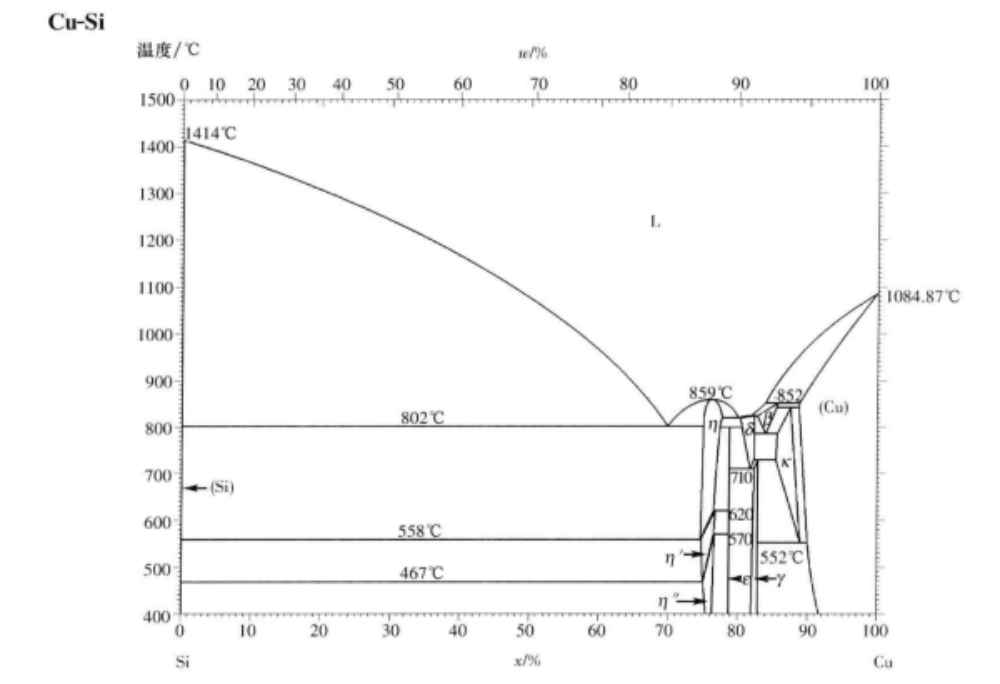
Melting point: 825 ℃
Density: 7.7-7.8
Molecular weight: 345.82
EINECS:235-286-8
Properties of copper silicide:
Copper silicide (Cu5Si), also known as pentacopper silicide, is a binary silicon compound of copper and a metal intermetallic compound. This means that its properties are between ionic compounds and alloys. This solid crystalline material is a silver solid that is insoluble in water. Has excellent conductivity, thermal conductivity, ductility, corrosion resistance, and wear resistance.
Preparation method:
Copper silicide can be prepared by heating a mixture of copper and silicon.
The use of copper silicide:
1) Due to its excellent conductivity, copper silicide is often used as a material for electronic components such as integrated circuits, circuit boards, and wires. Copper silicide thin films can be used to passivate copper based chips, suppress their diffusion and electron migration, and serve as diffusion barriers.
2) High temperature materials: Copper silicide has good high-temperature stability and is commonly used in high-temperature materials, which can maintain its physical and chemical properties unchanged in high-temperature environments.
3) Catalyst: Due to its unique chemical properties, copper silicide is also commonly used as a catalyst, especially in certain chemical reactions, which can improve reaction efficiency and selectivity.
Packaging and storage:
This product is packaged in an inert gas filled plastic bag, sealed and stored in a dry and cool environment. It should not be exposed to air to prevent moisture and oxidation aggregation, which may affect dispersion performance and usage effectiveness