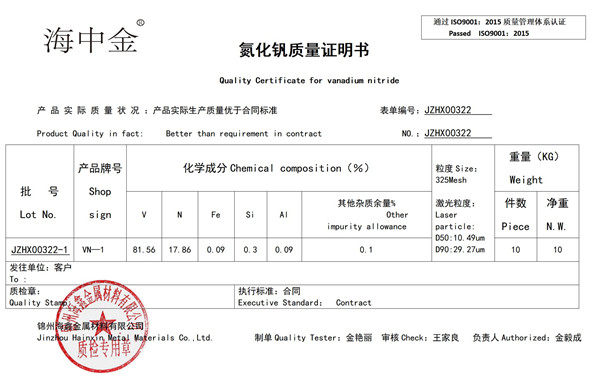
Vanadium Nitride(VN)


Properties: Black cubic crystalline powder
Density (g/ml, 25/4 ℃): 6.13
Melting point (º C): 2360
Resistivity( μ Ω•cm):85
Thermal conductivity (w/ (m • K)): 11.3
Volume expansion coefficient (k-1): 8.1 × 10—6
Microhardness (kg/mm2): 1310



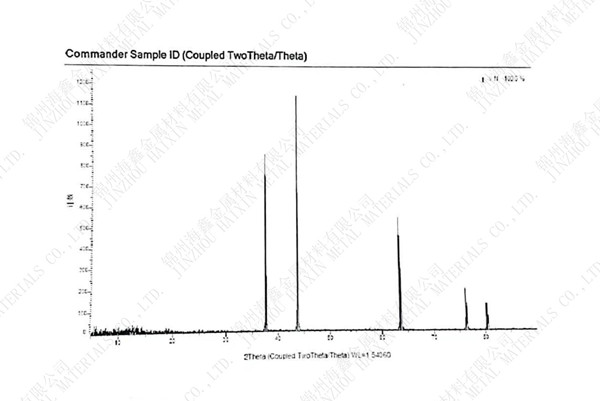



Structure introduction:
Vanadium nitride has two crystal structures: one is v3n, hexagonal crystal structure, with extremely high hardness, the microhardness is about 1900hv, and the melting point can not be measured; Second, VN, density 6.13 Relative molecular weight 64.95 [2] Face centered cubic crystal structure, the microhardness is about 1520hv, and the melting point is 2360 ℃. They all have high wear resistance.
Vanadium nitride, also known as vanadium nitride alloy, is a new type of alloy additive, which can replace ferrovanadium in the production of microalloyed steel. The addition of vanadium nitride to steel can improve the comprehensive mechanical properties of steel, such as strength, toughness, ductility and thermal fatigue resistance, and make the steel have good weldability. At the same strength, the addition of vanadium nitride can save 30-40% of vanadium, thus reducing the cost. Vanadium nitrogen alloy can be used in structural steel, tool steel, pipe steel, reinforcement and cast iron. The application of V-N alloy in high strength low alloy steel can effectively microalloy V and N at the same time, promote the precipitation of carbon, V and N compounds in the steel, and play a more effective role in precipitation strengthening and grain refinement.
V-N alloy has more effective strengthening and grain refining effect than FEV
The addition of vanadium can be saved by using vanadium nitrogen alloy. Compared with ferrovanadium, vanadium nitrogen alloy can save 20-40% vanadium under the same strength conditions. The use of vanadium nitrogen alloy can stabilize the yield of vanadium and nitrogen and reduce the performance fluctuation of steel.
It is very convenient to use vanadium nitrogen alloy with less loss. It adopts high-strength moisture-proof packaging and can be directly put into the furnace.
1. Vanadium nitride is a better steelmaking additive than high vanadium iron. Using vanadium nitride as an additive, the nitrogen component in vanadium nitride can promote the precipitation of vanadium after hot working, making the precipitation particles smaller, so as to better improve the weldability and formability of steel. Used as cemented carbide raw material to produce wear-resistant and semiconductor films. It is a new and efficient vanadium alloy additive, which can be used to produce high-strength low-alloy steel products such as high-strength welded reinforcement, non quenched and tempered steel, high-speed tool steel, high-strength pipeline steel, etc. Compared with FEV, V-N alloy can strengthen and refine grains more effectively, save 30% ~ 50% vanadium than FEV, and play a great role in improving the strength of steel and reducing the cost of steelmaking.
2. Used as cemented carbide raw material to produce wear-resistant and semiconductor films.
Synthesis method:
1. vanadium nitride can be prepared by fully mixing stoichiometric carbon and vanadium pentoxide, and carrying out reduction nitridation reaction at 1250 ℃ in chlorine atmosphere. It can also be prepared by reacting nitrogen hydrogen mixture with vanadium tetrachloride at 1400 ~ 1600 ℃; Or it is prepared by reacting ammonia (NH3) with ammonium metavanadate (NH4VO3) at 1000 ~ 1100 ℃.
2. reduction method is adopted. Vanadium nitride can be prepared by fully mixing stoichiometric carbon with vanadium pentoxide and reducing nitridation at 1250 ℃ in nitrogen atmosphere. It can also be prepared by reacting nitrogen hydrogen mixture with vanadium tetrachloride at 1400 ~ 1600 ℃; Or it is prepared by reacting ammonia (NH3) with ammonium metavanadate (NH4VO3) at 1000 ~ 1100 ℃.

