Molybdenum Boride(MoB)


.jpg)

.jpg)

.jpg)

Chinese Name: molybdenum borate
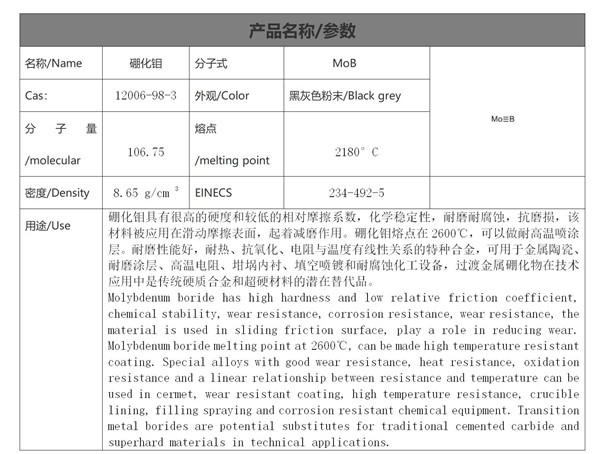
English Name: molybdenum boride
MOL File: 12006-98-3. mol
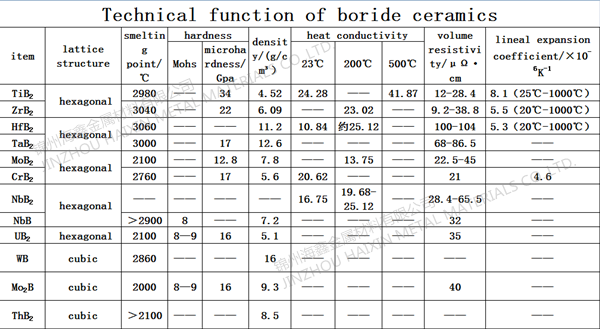
Density: 8.65 g/cm3 at 25 ° C
Molecular weight: 106.75
MOL File: 12006-98-3. mol
Melting point: 2180 ° C
Storage method: sealed in a cool and dry place, in a cool environment, not exposed
to the air, to prevent oxidation and agglomeration caused by moisture.
manufacturing method
1.Reduction method: boron oxide and molybdenum oxide are prepared by reduction
at high temperature in the presence ofcarbon
2.Molybdenum reacts with boron powder under vacuum at 1300 ~ 1400 ℃.
3. When boron is evaporated on molybdenum (or vice versa), molybdenum borate can
be formed on the interface.
Purpose:
1.Ceramic coating: molybdenum borate cermet has high hardness and low relative
friction coefficient. This material is applied to sliding friction surface to reduce wear.
For example, molybdenum borate coating is applied to the inner wall of engine cylinder
liner. At the same time, because the material has low reactivity with liquid zinc, it is
applied to the surface spraying material of continuous hot-dip galvanized submerged
roller abroad to protect the submerged roller from the corrosion of liquid zinc.
2. Molybdenum borate is used as a high-efficiency catalyst for polysulfide oxidation
and reduction in high-energy density lithium sulfur batteries. The high conductivity
and abundant catalytic active centers of molybdenum Borate Nanoparticles make lips
have rapid redox kinetics on a high sulfur loaded electrode (6.1 mg cm-2). In addition,
the hydrophilicity of molybdenum borate and its good wettability to electrolyte can
promote the penetration of electrolyte and the oxidation-reduction of lips, ensuring
a high sulfur utilization rate under the condition of dilute electrolyte.
3. Superhard materials: boride contains 4 to 5 boron atoms per molybdenum atom.
The Vickers hardness of MOB5 is 37 to 39gpa, which makes it a potential superhard
material.
Molybdenum borate plays an extremely important role in modern industry and is
widely used in alloy materials, coating materials, high temperature structural materials,
cathode materials, corrosion-resistant materials, wear-resistant materials and other fields.
4. Molybdenum borate powder is considered as a kind of wear-resistant and
corrosion-resistant material, and it is also an important component of iron and nickel boride
composite cermet materials.
5. The melting point of molybdenum borate is 2600 ℃, which can be used
as a high-temperature spray coating. Special alloys with good wear resistance, heat
resistance and linear relationship between resistance and temperature can be used in
cermet, wear-resistant coating, high-temperature resistance, pot lining, void filling spray
plating and corrosion-resistant chemical equipment. Transition metal borides are potential
substitutes for traditional cemented carbide and high hardness materials in technical
applications. And with the progress of science and technology, the application field of
molybdenum borate compounds will be further expanded. This material will show more
excellent application value and huge market prospect.