Molybdenum Silicide(MoSi2)

.jpg)


.jpg)
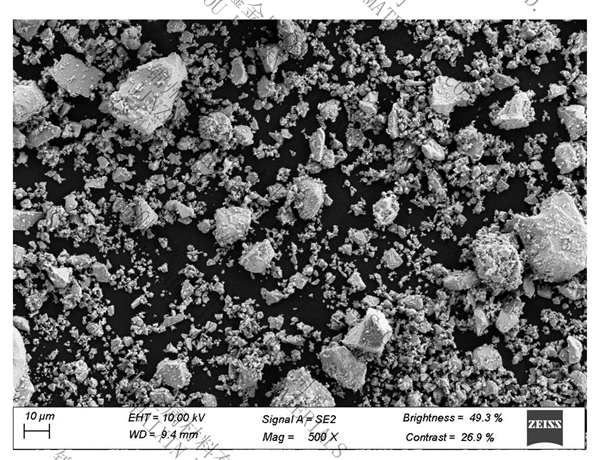
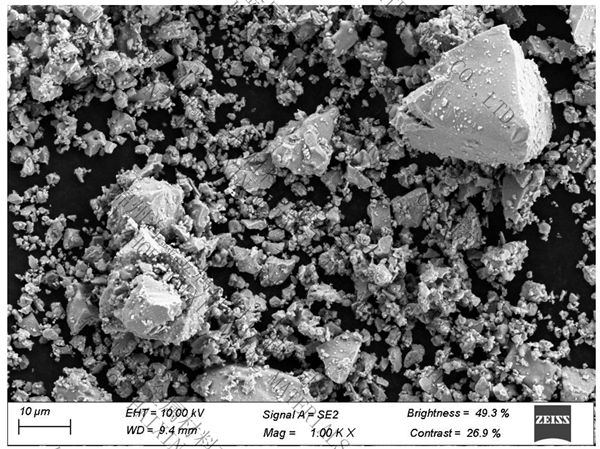
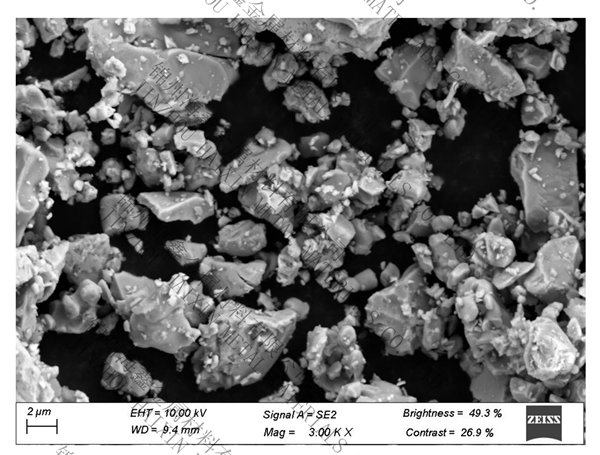
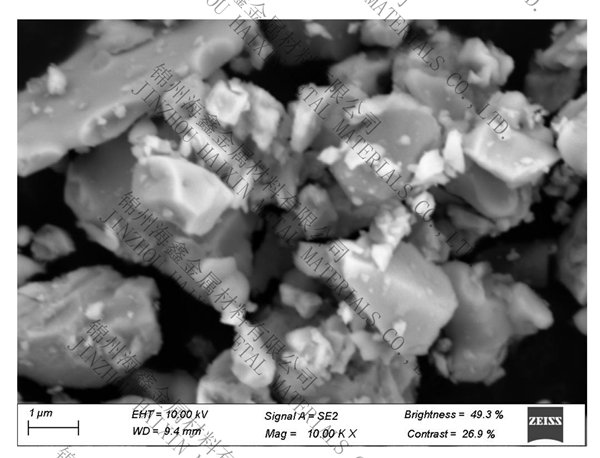






.jpg)

Chinese Name: molybdenum silicide
English Name: molybdenum silicide
Density: 6.31
Melting point: 1930 º C
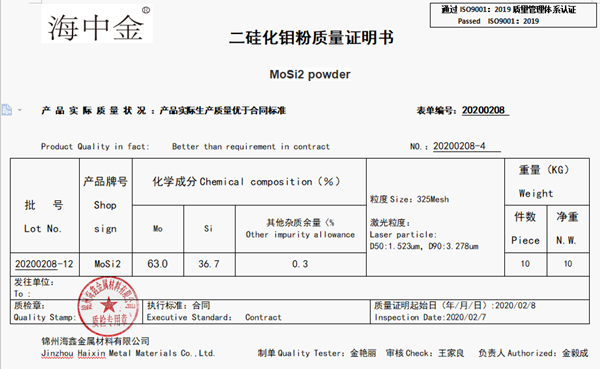
Molecular formula: MoSi2
Molecular weight: 152.13100
Accurate mass: 153.85900
Appearance: gray metal
Preparation principle: MoSi2 can be prepared by direct reaction of Mo + 2Si → MoSi2
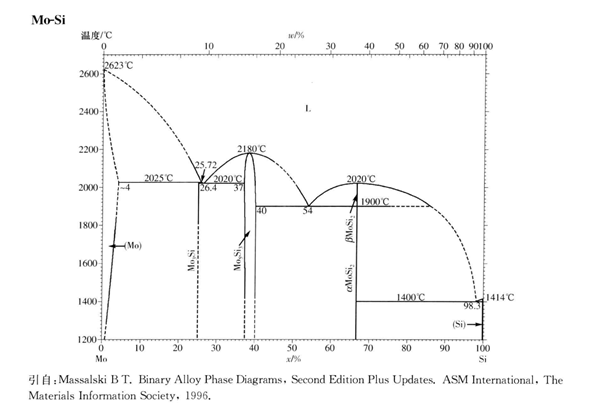
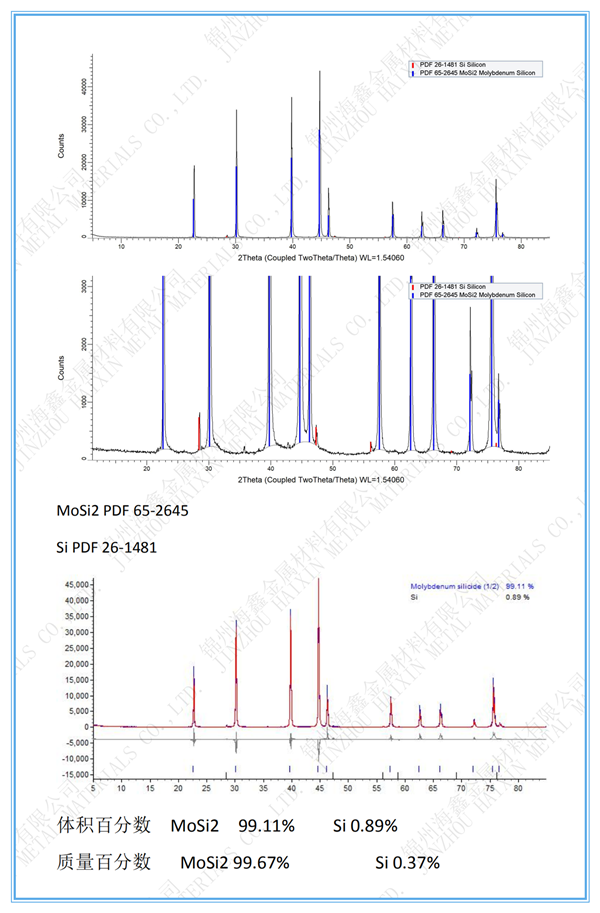
Molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) is a silicon compound of molybdenum. Because the radii of the two atoms are not much different and the electronegativity is close, it has properties similar to that of metal and ceramic. The melting point is as high as 2030 ℃, with conductivity. Under high temperature, a silicon dioxide passivation layer can be formed on the surface to prevent further oxidation. Its appearance is gray metal color, which originates from its four sides α- Type a crystal structure, also hexagonal but unstable β- Modified crystal structure. Insoluble in most acids, but soluble in nitric acid and hydrofluoric acid. MoSi2 is an intermediate phase with high silicon content in the Mo Si binary alloy system, and is a Dalton type intermetallic compound with fixed composition. It is a high-temperature material with excellent performance because of its dual characteristics of metal and ceramic. Good high-temperature oxidation resistance, the oxidation temperature is as high as 1600 ℃, which is equivalent to SiC; With moderate density (6.24g/cm3); Lower coefficient of thermal expansion (8.1 × 10-6K-1); Good thermal conductivity; The higher brittle ductile transition temperature (1000 ℃) has ceramic like hard brittleness. And exhibits metallic soft plasticity above 1000 ℃. Mosi is mainly used as heating element, integrated circuit, high-temperature anti-oxidation coating and high-temperature structural material. In MoSi2, molybdenum and silicon are bonded by metal bonds, and silicon and silicon are bonded by covalent bonds. Molybdenum disilicide is a gray tetragonal crystal. It is insoluble in general mineral acids (including aqua regia), but soluble in the mixed acid of nitric acid and hydrofluoric acid. It has good high-temperature oxidation resistance and can be used as a heating element working in an oxidizing atmosphere at high temperature (< 1700 ℃). In an oxidizing atmosphere, a protective film layer is formed on the surface of dense quartz glass (SiO2) burned at high temperature to prevent continuous oxidation of molybdenum disilicide. When the temperature of the heating element is higher than 1700 ℃, a SiO2 protective film is formed, fused at a melting point of 1710 ℃, and fused with SiO2 to form molten droplets. It loses its protection ability due to the action of its surface extension. Under the action of oxidant, when the elements are continuously used, the protective film is formed again. It should be pointed out that this element cannot be used for a long time in the temperature environment of 400-700 ° C due to the strong oxidation at low temperature.
Molybdenum disilicide is applied in the fields of high-temperature anti-oxidation coating materials, electric heating elements, integrated electrode films, structural materials, reinforcing agents for composite materials, wear-resistant materials, and connecting materials for structural ceramics, and is distributed in the following industries:
1) Energy chemical industry: electric heating elements, high-temperature heat exchangers of atomic reactor devices, gas burners, high-temperature thermocouples and their protective tubes, melting vessels and crucibles (used for smelting sodium, lithium, lead, bismuth, tin and other metals).
2) Microelectronic industry: MoSi2 and other refractory metal silicides Ti5Si3, WSi2, TaSi2, etc. are important candidates for gate and interconnect films of large-scale integrated circuits.
3) Aerospace Industry: as a high-temperature anti-oxidation coating material, it has been widely and deeply researched and applied. Especially as a material for turbine engine components such as blades, impellers, burners, tail pipes and sealing devices. Molybdenum disilicide, as a structural material, is used in high-temperature components of aviation and automobile gas turbines, gas burners, nozzles, high-temperature filters and spark plugs, and has become a hot topic in the research of intermetallic compound structural materials. The major obstacle in this application is its high room temperature brittleness and low high temperature strength. Therefore, low-temperature toughening and high-temperature strengthening of molybdenum disilicide are the key technologies for its practical application as a structural material. The research in this aspect shows that alloying and compounding are effective means to improve the room temperature toughness and high temperature strength of molybdenum disilicide. The components commonly used for molybdenum disilicide alloying are only a few silicides having the same or similar crystal junctions WSi2, NbSi2, CoSi2, Mo5Si3 and Ti5Si3 as molybdenum disilicide, among which WSi2 is ideal. However, alloying with WSi2 will obviously lose the advantages of molybdenum disilicide in specific gravity, and its application will be limited to a certain extent. Practice has proved that molybdenum disilicide has good chemical stability and compatibility with almost all ceramic reinforcements (such as SiC, tic, ZrO2, Al2O3, TiB2, etc.). Therefore, compounding is an effective way to improve the mechanical properties of molybdenum disilicide.
4) Automotive Industry: turbocharger rotor, valve body, spark plug and engine parts for automotive engines.
Storage method:
This product should be sealed and stored in a dry and cool environment. It should not be exposed to the air for a long time to prevent agglomeration due to moisture, which will affect the dispersion performance and use effect. In addition, it should avoid heavy pressure and contact with oxidant. It should be transported as ordinary goods.